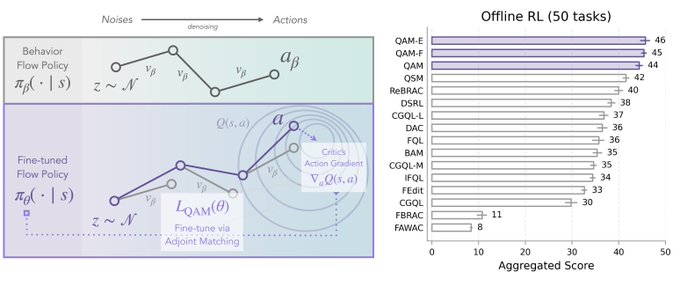
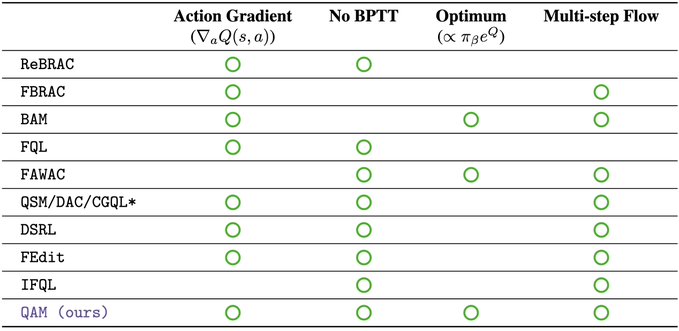
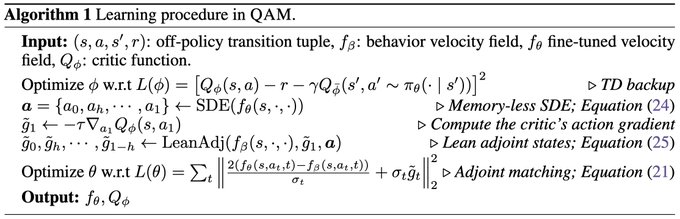
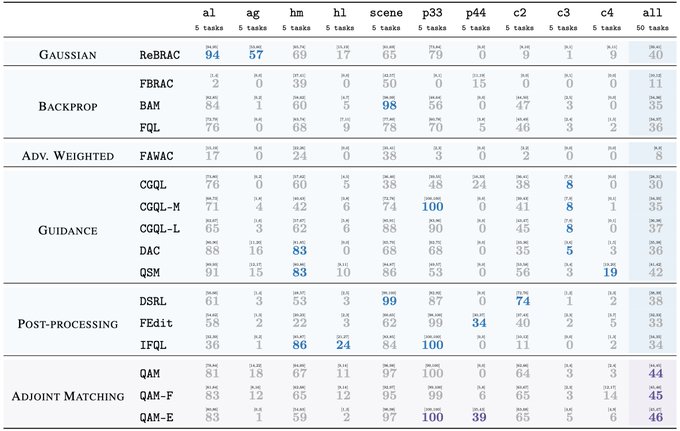
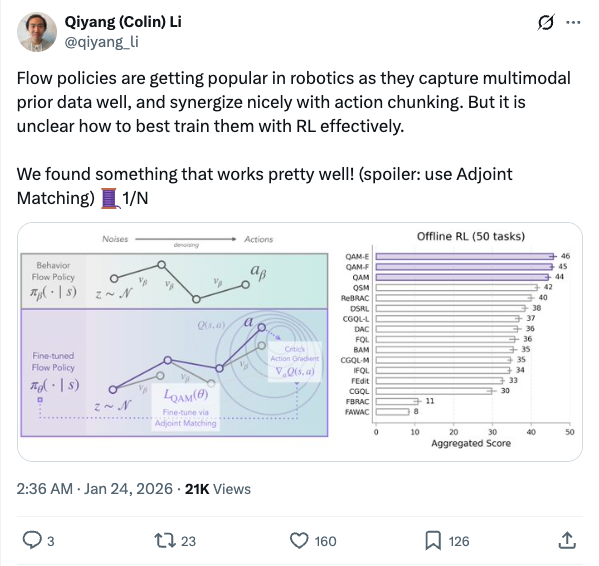
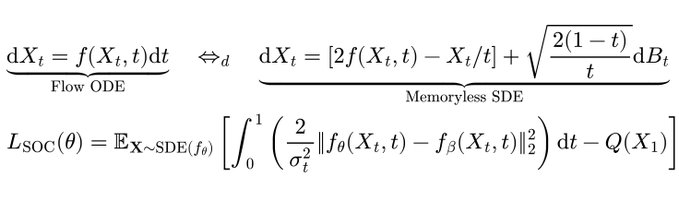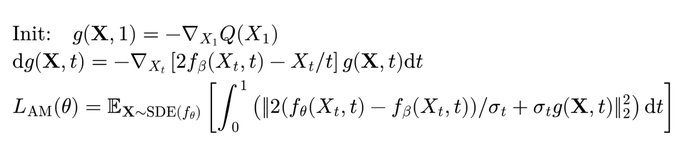🧵 Flow policies are getting popular in robotics as they capture multimodal prior data well, and synergize nicely with action chunking. But it is unclear how to best train them with RL effectively. We found something that works pretty well! (spoiler: use Adjoint Matching) 1/N 🧵 In RL, especially with prior data, we often want to find a policy that maximizes some value function (e.g., Q) while staying close to a behavior policy (via a KL constraint). The challenge is to find this optimal behavior-constrained policy as fast as possible. 2/N 🧵 Prior methods often hit at least one of these pitfalls: (1) don't use the gradient of Q, (2) requires unstable backprop through multi-step flow, (3) don't recover the optimal behavior-constrained policy at optimum, (4) sacrifice policy expressivity via distillation. 3/N 🧵 It turns out that Adjoint Matching, a recently proposed technique from the flow-matching generative modeling literature is perfectly suited for solving these issues all at once in RL! How does Adjoint Matching work? Let's dive in! 4/N 🧵 Actions from a flow policy are generated by integrating Gaussian noises through an ODE. We can construct an SDE that results in the same marginal distribution and use this SDE to reformulate the constrained optimization problem above as a stochastic optimal control objective! 5/N 🧵 Solving this new objective seemingly requires us to backprop through an SDE, causing potential instability issues. In Adjoint Matching, Domingo-Enrich et al., use a reverse ODE to construct an objective with the same optimum but without direct backprop! 6/N 🧵 Applying this to RL yields our algorithm QAM. It avoids all prior issues: we use the action gradient from Q to directly fine-tune a flow policy towards the optimal behavior-constrained policy without using unstable backprop or sacrificing policy expressivity. 7/N 🧵 In practice, we also find that it is often beneficial to relax the KL constraint such that the fine-tuned policy can output actions that are close "geometrically" close to the behavior actions in the prior data but have low probability under the behavior distribution. 8/N 🧵 We experiment with two variants. The first variant trains a FQL policy on top of QAM's fine-tuned policy. The second variant trains a residual policy to refine the action samples from QAM's fine-tuned policy. We call these two QAM-F and QAM-E (E for edit) respectively. 9/N 🧵 We evaluated QAM on OGBench, a popular offline RL benchmark with a diverse set of long-horizon challenging tasks ranging from locomotion to manipulation. All three variants of QAM exhibit strong performance. 10/N 🧵 We also find the QAM-E variant is particularly well-suited for online fine-tuning. On some of the hardest domains from the benchmark, our method exhibits strong sample-efficiency and robustness across the board. 11/N 🧵 That is all! This project has been a fun journey in searching for a flow + RL method that brings the best of prior methods. And it would not be possible without my amazing advisor @svlevine !! Code+exp data: http:// github.com/colinqiyangli/ qam … Paper: https:// arxiv.org/abs/2601.14234 12/N=12
Thread Screenshots
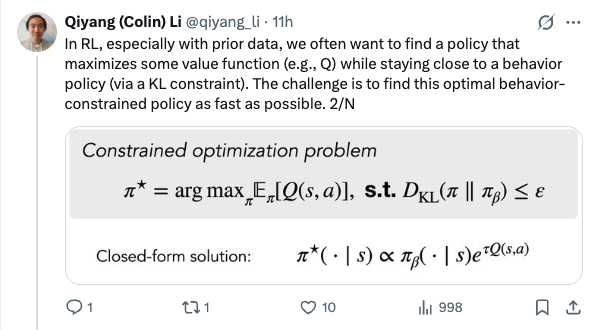
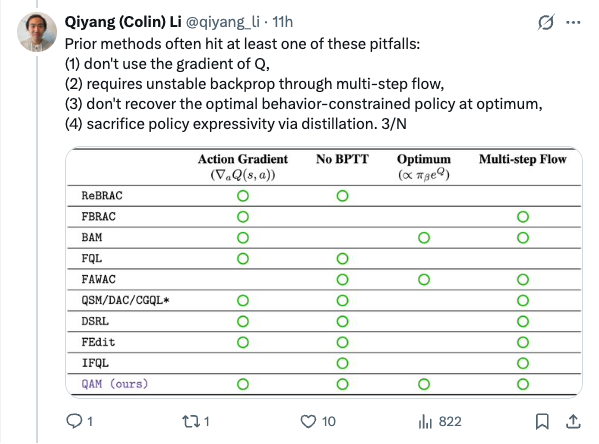






Images